[Depth] How the RMB transforms into the "international currency" game pricing power

Without the cross-border RMB capital market that the “banker†can dominate, it will become the real stage for the future RMB exchange rate to find “market equilibriumâ€.
For the financial market and monetary policy regulators, this round of RMB exchange rate decline has long been expected. The central bank sold nearly $600 billion in just one year to intervene in the foreign exchange market. "This is unprecedented in global financial history."
Small-scale "encounter encounter"
Since the exchange reform, China's financial regulatory authorities have greatly strengthened their control over the liquidity of the offshore market. The “sniper†of offshore arbitrage capital has become increasingly accurate, and the short-sellers who dare to take risks and “be gambling†with the Chinese central bank are decreasing.
On October 25, 2016, the China Foreign Exchange Trading Center announced that the RMB exchange rate was reported at 6.7744, a new six-year low. Less than a month since September 30, the spot exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar has fallen by more than 1,000 basis points, depreciating more than 1.5%. Some analysts said that the depreciation is mainly guided by the central bank's central price, and the depreciation trend may continue.
The continuous decline of the RMB exchange rate has caused the public, who originally only focused on the stock market and real estate, to begin to fall into unease. The interpretation of various RMB exchange rates on Weibo and WeChat was screened, and the highly professional topics such as currency and exchange rate suddenly entered the public eye.
But for financial markets and monetary policy authorities, this round of RMB exchange rate decline has long been expected. The depreciation of the fourth round of exchange rates, both in terms of market expectations and policy responses, is more fully prepared than the three rounds of depreciation experienced since the August 2015 exchange rate reform.
On the morning of October 21, when the central parity of the RMB exchange rate was sharply lowered, the State Administration of Foreign Exchange spokesperson Wang Chunying provided a set of key data interpretations for the market at the press conference: from the exchange rate adjustment, in this round of US dollars plus In the global exchange rate adjustment triggered by interest expectations, the exchange rate of the euro, the pound and the yen against the US dollar depreciated by 2.8%, 5.6% and 2.5% respectively; in contrast, the RMB exchange rate only fell by about 1% against the US dollar, while maintaining a basket of exchange rates. appreciation.
In terms of cross-border capital flows, the pressure on foreign exchange outflows brought about by the early repayment of US dollar debts by enterprises has been significantly weakened. Since 2016, the bank's foreign exchange settlement and sales deficit has narrowed from US$124.8 billion in the first quarter to US$69.6 billion in the third quarter. At the same time, bank foreign exchange receipts and payments have changed from a deficit of US$36.6 billion in the first quarter to a surplus of US$17.6 billion in the third quarter.
This data seems to indicate that the vicious circle of "the depreciation of the renminbi - capital outflow - the decline of foreign reserves" that had been most worried about the market before did not appear. A series of cross-sectoral liquidity regulatory measures launched by the financial regulatory authorities in the early stage effectively controlled the gray channel of arbitrage hot money.
Wang Chunying also said that with the further opening of the domestic bond market, the gradual implementation of the macro-prudential management policy of full-scale cross-border financing, and the increase in the demand for offshore entities to allocate RMB assets after the RMB officially joined the SDR (Special Drawing Rights), the future foreign exchange market A series of positive factors in the structure will continue to promote the balance of foreign exchange supply and demand.
Hong Wei, chief China strategist of Bank of Communications International, previously pointed out that the sharp drop in the RMB exchange rate during this round was mainly due to the “filling down†of the expected increase in the US dollar rate hike during the National Day, and market researchers including him generally believed that the central bank explicitly released Continue to push forward the signal of exchange rate reform.
Other market observers, including the research firm Anbang think tank, are worried that the US dollar interest rate hike is expected to once again trigger the gathering of international "RMB shorts" in the face of high corporate debt leverage. If the market expectation cannot be effectively managed and guided, the risk of arbitrage capital shorting the RMB triggering “capital outflow + RMB depreciation†still exists.
In the “bridgehead†of the RMB exchange rate game – the offshore RMB market in Hong Kong, China’s financial management and international arbitrage capital have launched a small “encounter encounterâ€. On October 11, the Hong Kong interbank RMB overnight and one-week lending rates both hit a high since September 20, and the market is regarded by the four major banks as the “incitement†to deter the international shorts by recycling liquidity. Since the short-term arbitrage capital mainly borrows the short-term exchange rate of RMB, the increase of the lending rate means that the short-selling cost is greatly increased. Since the exchange reform, the Chinese financial regulatory authorities have strengthened their control over the liquidity of the offshore market by strengthening a series of policies such as capital project control and combating foreign exchange crimes. The “sniper†of offshore arbitrage capital has become increasingly accurate. From the beginning of the year, the RMB borrowing overnight interest rate was 66.82%, the highest point in the middle of September was 23.68%, and then the overnight interest rate adjustment was only 2.82%, showing that it is adventurous to “be gambling†with the People’s Bank of China. The short position is gradually decreasing - in a sense, this is also one of the "cards" of the central bank to continue to promote exchange reform in the process of this round of RMB exchange rate decline. The SAFE spokesperson’s analysis of the favorable factors for promoting the balance of foreign exchange supply and demand shows that after the entry of SDR, the reform of the RMB exchange rate mechanism, which has been slowed down several times due to multiple factors inside and outside, may once again usher in the “opportunity window†for reform and promotion. ".
Game pricing power
From the official mid-price to the market closing price, from benchmarking the “one-on-one exchange rate†to introducing “a basket of currenciesâ€, from the onshore price regulation to the offshore price game, China’s efforts in the formation mechanism of the RMB exchange rate are painstaking. .
As early as the morning of August 11, 2015, the People's Bank of China announced that it would adjust the formation mechanism of the RMB against the US dollar to achieve the “consolidation†of the RMB central price and the market closing price, and depreciate the RMB by 3% at a time to “correct the deviationâ€. . According to Zhang Xiaohui, assistant to the central bank governor, the central bank will no longer set the renminbi control points after the exchange reform. In addition to the short-term interventions during abnormal fluctuations, market-based transactions will form the “balanced price†of the RMB exchange rate.
However, under the influence of panic sentiment and excess liquidity after the stock market crash, the RMB depreciation under market-based pricing rules is expected to rapidly “self-reinforceâ€, and at the same time, in the mode of maintaining stable exchange rate through market transactions, the huge consumption of foreign exchange reserves is also It has attracted market concerns about the central bank’s “safeguard boundary for external reservesâ€.
The attempt to reach a “balanced exchange rate†near the one-off depreciation was frustrated, and the central bank had to maintain the stability of the market closing price through the huge foreign exchange transactions of the commercial banking system.
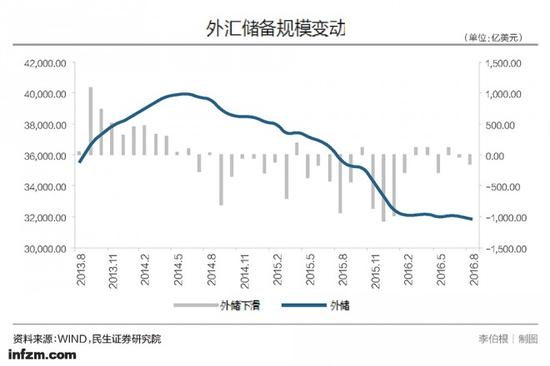
According to the US Treasury's "International Economic and Exchange Rate Policy Report", from August 2015 to August 2016, China sold a total of about 570 billion US dollars in foreign exchange assets, "to prevent the devaluation of the renminbi."
This market-oriented "exchange rate support" has won international recognition including the United States, and complies with the IMF (International Monetary Fund) requirements for the RMB to join the SDR currency basket, but also brings China's foreign exchange reserves. A huge loss of pressure - in the last two months of 2015 alone, the central bank's external reserves decreased by nearly 200 billion US dollars.
At the same time, in the case of a sharp depreciation of the global currency against the US dollar, the appreciation of the RMB against the “US dollar exchange rate†against other currencies has also damaged the export competitiveness of Chinese companies.
In this context, the renminbi had to introduce a “secondary exchange reformâ€. The foreign exchange trading center launched the CFETS (RMB exchange rate index) on December 11, 2015, and announced the calculation method and weight of the index, guiding the market to focus only on the “bilateral exchange rate†between the RMB and the US dollar, and turned to the concern including the US dollar, the euro and the Japanese yen. A basket of exchange rates, including currency.
After New Year's Day in 2016, the RMB immediately began a large adjustment between the US dollar exchange rate and the “a basket of exchange ratesâ€. While the RMB exchange rate index for CFETS remained relatively stable, the central parity of the US dollar continued to drop sharply.
At the same time that the pressure on the depreciation of the renminbi against the US dollar was quickly released, the atmosphere of the offshore renminbi market was also at its peak. At the beginning of January 2016, the gap between the onshore and offshore RMB exchange rates reached a record of nearly 1300 points, and a large number of international short-sellers began to gather in the Hong Kong market.
For the financial market and monetary policy regulators, this round of RMB exchange rate decline has long been expected. The central bank sold nearly $600 billion in just one year to intervene in the foreign exchange market. "This is unprecedented in global financial history."
At a time when a "short renminbi" war is about to break out, short-sellers suddenly find that the liquidity of the offshore renminbi market has been drained. Hong Kong interbank RMB overnight interest rates continued to rise, and on January 12 once rushed to an unprecedented high of 66.8%.
The rise in the offshore RMB market interest rate, while pushing up the appreciation of the offshore RMB exchange rate, also caused the market institutions that had shorted the RMB in the early stage to suffer heavy losses. Coupled with the weakening of the expected appreciation of the US dollar, the pressure on the loss of foreign exchange reserves in the following months has been greatly reduced, and even a slight increase has occurred.
After the Spring Festival of 2016, the new RMB exchange rate pricing mechanism has gradually stabilized. In the view of Zhong Zhengsheng, head of macro research at Caixin Think Tank, this exchange rate mechanism with the “closing exchange rate + a basket of currency exchange rate changes†is in line with the “management floating†renminbi exchange reform direction, and The formation of effective communication in the market has become an important mechanism for the central bank to guide the “strategic depreciation†of the RMB exchange rate.
However, in the view of Zhang Ming, director of the International Investment Research Office of the Institute of Social Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, the RMB exchange rate price formed by this “closing price + basket currency†mechanism is actually “two exchange rate formation mechanismsâ€: the former is global capital. The “transaction price†under the flow, while the latter mainly reflects the “trade balance†under the trade deficit of each country.
In Zhang Ming's view, because the speed of capital flow is much higher than the change of trade balances of various countries, under the premise of China's capital outflow, the "transaction price" represented by the closing price will continue to pull the "a basket of currencies" exchange rate representing the trade balance. Falling.
In other words, the “protection index†of the RMB exchange rate has changed from the high US dollar exchange rate to the lower “one basket exchange rateâ€. Although it has alleviated the consumption pressure of the huge extra storage, it has not formed a real “market equilibriumâ€. Once the external market turmoil or internal economic recovery is weak, the renminbi pegged to “a basket of exchange rates†may still face huge “protection pressureâ€.
In the switch from “nailing the US dollar†to “nailing a basket of exchange ratesâ€, the central bank sold nearly 600 billion US dollars in just one year to intervene in the foreign exchange market. Zhang Ming said frankly, “This is unprecedented in global financial history. of".
It is imperative to continue to use the huge extra reserves to “protect the exchange rateâ€. If we do not use foreign exchange reserves, how can the RMB exchange rate find its own "market equilibrium" without causing market panic, and where is the "fulcrum" of this market equilibrium?

SDR new pattern
China’s share of global trade continues to rise, and the renminbi continues to depreciate against a basket of currencies “lack of fundamental supportâ€.
The exchange rate of RMB exchange rate from “official price†to “market price†and the move by the People’s Bank of China to use the huge extra reserve as the “protection†of the RMB exchange rate have made domestic and foreign observers generally believe that the Chinese government will not maintain economic growth. Speed ​​up the "competitive depreciation."
While China’s share of global trade continues to rise, many researchers, including Ding Shuang, head of research at Standard Chartered Bank Greater China, believe that the renminbi continues to depreciate against a basket of currencies “lack of fundamental supportâ€.
Many researchers believe that the “turning point†of the scale of foreign exchange reserves in 2014 and the trend of capital outflows represented by them are the biggest “suspects†to promote this round of RMB depreciation.
Peng Xingyun, chief economist of First Venture Securities, pointed out that in the 14 years from January 2001 to June 2014, only 14 months of net storage decreased, and from July 2014 to August 2015 In the middle of the month, there have been 12 months of decline. He thus concluded that "China's foreign exchange reserves have undergone a trend change."
Standard Chartered Bank’s statistics show that in the 12 months after July 2015, on the eve of the exchange rate, while the foreign exchange reserves accelerated, the RMB depreciated by 7% and 10% against the US dollar and the Bank’s “a basket of currenciesâ€. %. It is also the phenomenon that this decline in foreign reserves is synchronized with the depreciation of the currency, which has caused market observers to worry about the “vicious circle†of capital outflows and currency depreciation.
According to the estimation of “hot money†by Peng Xingyun's research team, since the second half of 2014, there has been a continuous “hot money†outflow in China, but because of its “hot money†indicator, medium and long-term foreign exchange debts of domestic enterprises have not been excluded, including real estate. The scale of repayment of US dollar debts by many companies, including the industry, has also been included in the “hot moneyâ€.
Standard Chartered Bank’s research report believes that the “main force†of capital outflows since last year should be the adjustment of the asset-liability structure of the corporate sector: while prepaying foreign currency debts in advance, large-scale acquisition of foreign assets to hedge against the risk of appreciation of the US dollar.
This is also the reason why the SAFE spokesperson stressed that “pre-enterprise accelerated repayment of US dollar debt†brought about a significant weakening of foreign exchange outflow pressure, and the balance of foreign exchange inflows and outflows in the banking system.
While capital flows are gradually becoming more balanced, another market structure change that profoundly affects the fundamentals of the RMB exchange rate has quietly surfaced, that is, the emergence of cross-border RMB capital markets.
On October 1, 2016, the official inclusion of the RMB in the SDR currency basket marked the status of the RMB as an international reserve currency. Although there is still a long way to explore between the nominal reserve currency and the substantial reserve currency, the establishment of this status shows that the pricing mechanism of the RMB exchange rate must continue from the “country currency†to the “international currencyâ€. Transformation.
As a key mechanism for this transformation, the Chinese government and the monetary authorities have worked hard for many years to build an unprecedented “cross-border RMB capital marketâ€, which includes both the RMB global clearing system developed by the central bank itself and the banks open to overseas central banks. Inter-bond and foreign exchange markets, as well as a series of new mechanisms for development and improvement, such as the currency swap mechanism and the offshore RMB bond market.
In Peng Xingyun's view, the RMB has become the fifth largest trade settlement currency in the world. At the end of 2014, when foreign investors held domestic RMB financial assets of up to 4.5 trillion yuan, the establishment of this “cross-border RMB capital market†was positive. It marks the efforts of the renminbi moving towards the international reserve currency to get rid of the "dollar shadow" role.
At the beginning of the creation of the “cross-border capital marketâ€, the scale of the offshore RMB market was also expanding rapidly. BNP Paribas interest rate strategist Ji Tianhe observed that from October 2015 to August 2016, the total net outflow of RMB was as high as 1.7 trillion yuan. At the same time, the renminbi that flows out is no longer reflected in deposits, but is converted into other assets.
Combined with the increase in domestic bonds held by overseas institutions in September to 385.97 billion yuan, the growth rate exceeded the average of the first eight months. Ji Tianhe concluded that before and after the RMB joined SDR, overseas central banks and institutions were buying RMB assets such as inbound bonds. To adjust the asset allocation under the new SDR basket. Statistics show that the amount of RMB settlement in global trade increased from 2.08 trillion yuan in 2011 to 7.23 trillion yuan in 2015. According to Standard Chartered Bank, after the SDR is officially in force, at least 1 trillion US dollars of global foreign exchange reserves will be converted into RMB assets in the future.
This rapidly growing “cross-border renminbi capital market†has changed the traditional “exchange rate game†model. On the one hand, when arbitrageurs try to short the RMB exchange rate, they will find that they are not facing the Chinese central bank, but the “opponent disk†of other central banks and RMB market investors; on the other hand, facing the increasingly large scale With the offshore RMB “capital pool†and cross-border RMB channel, it is difficult for the People’s Bank of China to take the market’s $200 billion sell-off to take advantage of the liquidity of the offshore RMB market.
This cross-border RMB capital market without the “banker†can be the real stage for the future RMB exchange rate to find “market equilibriumâ€.
In the new exchange rate equilibrium and global asset allocation process, the RMB exchange reform has been extended from the reform of the exchange rate pricing mechanism to the continuous exploration and improvement of the new financial market rules and structures.
With the emergence of the market-based pricing of the RMB exchange rate and the emergence of a new equilibrium mechanism, the need for the central bank to maintain “monet security†with high foreign exchange reserves is also declining. The huge foreign exchange reserve has reduced the credit efficiency of commercial banks in the form of high deposit reserve while allowing the central bank to passively release the amount of base money. This has distorted the price transmission mechanism of the financial capital market and the monetary policy operation of the central bank.
With the decline in foreign exchange reserves, the central bank cut the deposit reserve ratio six times in this round of economic downturn, releasing abundant liquidity for the domestic financial market, and also promoting the large-scale fiscal system reform including local debt replacement. .
Peng Xingyun believes that as the scale of foreign reserves continues to decline and the internationalization of the RMB further deepens, the statutory reserve ratio of Bank of China (3.390, 0.00, 0.00%) will fall to 5% or less in the next decade or less.
At the same time, the trillions of foreign reserves “wealth†formed by China’s export accumulation over the past 20 years have not disappeared. Instead, the company’s overseas investment and the foreign currency asset allocation of its residents have gradually formed a “national asset†throughout the world. Along with the downward trend of the government's external reserves, it will be an increase in the share of Chinese enterprises and residents in China's “overseas total assetsâ€.
However, under the multiple risk factors of global economic turmoil and structural transformation of the domestic economy, the ideal transformation of the internationalization of the RMB still faces many challenges and uncertainties.
On June 23, the outbreak of the "Black Swan" referendum on the Brexit vote again pushed the RMB exchange rate to the forefront. The pound and the euro hit 11.9% and 3.5% respectively in two trading days, while the US dollar and the yen rose 3.5% and 4.4% respectively as safe-haven assets.
The exchange rate differentiation in "a basket of currencies" has caused the renminbi that has not yet had "safe haven assets" credit to appear double depreciation against the US dollar and "a basket of currencies", so that the central bank has to start intervening in the market again at the psychological barrier of 6.7, and announced Since August 15, a foreign exchange risk reserve of 20% will be charged for overseas forward sales.
This new "double depreciation model" has once again triggered market concerns about the risk of "strategic depreciation" out of control. Many market researchers including Zhong Zhengsheng pointed out that in the process of returning RMB exchange rate to "market equilibrium", it is possible There is a “multiple equilibriumâ€. Once the market is expected to be mismanaged, there may be a “bad balance†risk of “selling RMB assets†and depreciating expectations.
In addition to external market turmoil, the domestic market is also facing depreciation pressure due to credit expansion. Standard Chartered Bank's research report pointed out that if state-owned enterprises and the banking industry cannot promote substantive reforms in the next few years, the asset bubble formed by the rapid growth of credit will damage domestic and foreign competitiveness, and prompt domestic residents to accelerate their shift to dollar asset allocation. It will bring greater depreciation pressure to the renminbi.
At the same time, the new mechanism of RMB global asset allocation, including Shanghai and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect, is constantly being explored and promoted. As Li Xiaojia, president of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, said, this is the first time that foreign assets have been denominated in renminbi to the domestic investors. It also means the opening of international asset allocation channels through renminbi investment.
For ordinary Chinese residents, simply changing the renminbi into the US dollar for "diversified allocation" is still a "difficult to please" option. With the formation of “cross-border RMB capital market†and the continuous improvement of relevant market rules and service systems, the allocation of overseas assets by means of RMB investment is no longer “unreachableâ€.
Advantage:
1. Energy-saving
It can be used together with temperature controller to form infrared radiant heating system. According to the temperature needs of the user, the temperature in each room can be freely adjusted. When the indoor temperature reaches the preset temperature, the heating system will automatically stop and the heat accumulator begins to emit heat so as to maintain the preset temperature for a long time, saving energy and power.
2. Environmenal protection
Its energy is electricity so that is very evironmental.
3. Safety and comfortable
It won't explode or emit odor, wind or noist.
4. Long life expectancy
It can be used more than 20 years.
5. Health care
The heat radiant can change body microcirculation, cell organization under skin producing resonance, clearing the barrier of microcirculation, adjusting and balancing nervous system promoting metabolism, increasing body physical power. It is very good for your health.
Ceiling Mounted Infrared Heater
Ceiling Mounted Infrared Heater,Ceiling Panel Heater,Ceiling Mounted Electric Heater,Ceiling Mounted Room Heater
Shandong Dexiang Electrical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.infraredroomheater.com